Brown Sugar Drugs Addiction – Causes, Symptoms And Treatment
When we hear about brown sugar addiction, it is important to distinguish it from the ordinary brown sugar we use at home. This Brown sugar, in the context of addiction, refers to an adulterated form of heroin. Unlike the natural sweetener, this brown sugar contains approximately 20% heroin.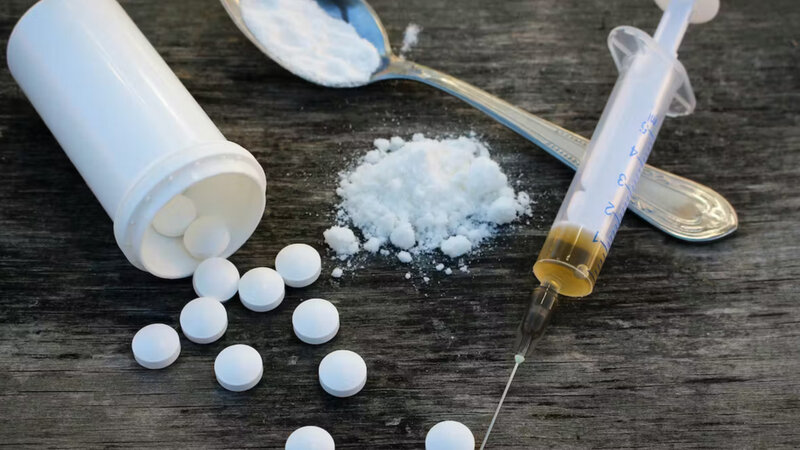
It is worth noting that pure heroin constitutes only a small portion, around 20%, of the brown sugar drug. The remaining 80% is made up of adulterants like chalk powder, zinc oxide, and even substances like iodex.
These impurities are added to the drug to reduce its production cost since genuine brown sugar, in its pure form, is highly expensive. Unfortunately, this means that consumers who use brown sugar are unknowingly ingesting a poisonous substance that gradually damages their health.
While pure brown sugar can be snorted, the majority of users obtain the impure form, which burns at a lower temperature. Consequently, many individuals prefer to smoke it rather than snort it in order to achieve the desired effects.
Additionally, some people choose to inject brown sugar using a syringe, a highly dangerous method due to the incomplete dissolution of impurities. To enable injection, brown sugar is typically dissolved in a citric acid component since it does not readily mix with water.
In India, the use of brown sugar has been rapidly increasing, particularly in some parts which signifies a concerning trend. Once consumed, brown sugar quickly affects the user, directly impacting their metabolism and initiating a range of harmful effects.
The effects typically manifest within a minute of consumption and can last for approximately 4-5 hours. It is crucial to understand that these effects are detrimental to the user’s well-being and overall health.
Causes of Brown Sugar Addiction
Here are some of the common causes of brown sugar addiction:
1. Lack of control: Addiction involves a loss of control over one’s actions. Individuals addicted to brown sugar find it difficult to stop or limit their drug use, even in the face of negative consequences.
2. Medicinal and recreational use: Some people initially use drugs, including brown sugar, for medicinal purposes, such as pain management prescribed by healthcare professionals. Others may use drugs recreationally for pleasure or to escape from stress and emotional difficulties.
3. Physical factors: The repetitive use of drugs like brown sugar can lead to physical dependence, where the body adapts to the drug’s presence and requires it to function normally. This physical dependence can contribute to the development of addiction.
4. Surrounding factors: The environment and social surroundings play a significant role in addiction. If an individual is exposed to a drug-using community or influenced by peers who engage in drug use, they may be more likely to develop an addiction.
5. Environmental factors: The overall environment in which a person resides, including factors like drug availability and societal norms around drug use, can influence the likelihood of addiction. Living in an environment where drug use is prevalent can normalize and reinforce the behavior.
6. Family and emotional factors: Family dynamics and upbringing can contribute to addiction. If a child grows up in a family where drug use is normalized or witnessed as a coping mechanism, they may be more susceptible to addiction later in life. Emotional factors like stress, trauma, or untreated mental health conditions can also contribute to substance abuse.
7. Brain chemistry: The brain plays a crucial role in the development of addiction. The repetitive use of drugs, including brown sugar, can alter brain chemistry and lead to dependence. The brain adapts to the presence of the drug and responds to it as if it were a normal chemical secretion, reinforcing the desire to use the drug.
8. Loss of voluntary control: Addiction occurs when an individual loses voluntary control over their drug use. Once addiction sets in, the individual’s ability to stop or control their drug intake becomes significantly impaired.
Understanding these causes can help inform prevention strategies, early intervention efforts, and effective treatment approaches to address brown sugar addiction.
Symptoms Of Brown Sugar Addiction
Here are some of the common symptoms of brown sugar addiction:
1. Immediate symptoms: Immediate symptoms of brown sugar addiction can be observed after the first-time use or infrequent use. These symptoms may include:
- Vomiting and nausea
- Headache
- Itching
- Redness of the skin
- Frequent dry mouth
2. Short-term symptoms: As the body becomes more accustomed to brown sugar use, short-term symptoms may become more apparent. These symptoms can include:
- Foggy mental state or confusion
- Slowed breathing
- Fatigue and getting tired easily, even with minimal physical exertion
- Drowsiness and excessive sleepiness
3. Long-term symptoms: With continued and increased abuse of brown sugar, long-term symptoms can manifest. These symptoms may include:
- Frequent drug stealing or engaging in deceptive behaviors to obtain the drug
- Aggressive behavior and irritability
- Collapsed veins due to repeated injection use
- Skin problems, such as infections, sores, or scarring from drug use
- Diseases affecting the liver, kidneys, and heart due to the toxic effects of brown sugar on these organs
Note: It’s important to note that the symptoms and their severity can vary depending on factors such as the individual’s overall health, the frequency and duration of brown sugar use, and the presence of any underlying physical or mental health conditions.
Recognizing these symptoms can help in identifying a potential addiction and seeking appropriate professional help and support for individuals struggling with brown sugar addiction.
Withdrawal Symptoms Of Drug Addiction
Here are some of the withdrawal symptoms associated with brown sugar addiction:
1. Sense of dependency: Brown sugar abusers can develop a strong sense of dependency on the drug. This means that their body and mind become reliant on the drug to function normally, and attempting to quit or reduce its use can lead to withdrawal symptoms.
2. Violent and aggressive behavior: During the withdrawal process, individuals addicted to brown sugar may experience episodes of violent and aggressive behavior. This can be a result of the body craving the drug and reacting negatively to its absence.
3. Unexpected weight loss: One of the physical effects of brown sugar addiction is unexpected weight loss. When an individual stops using the drug and enters the withdrawal phase, they may continue to experience weight loss as the body adjusts to functioning without the drug.
4. Loss of appetite: Withdrawal from brown sugar addiction can lead to a loss of appetite. The individual may have difficulty feeling hungry or may have a reduced desire to eat, resulting in further weight loss.
5. Insomnia: Insomnia, or difficulty sleeping, is a common withdrawal symptom experienced by individuals trying to quit brown sugar addiction. Sleep disturbances can occur as the body tries to readjust to normal sleep patterns without the influence of the drug.
6. Depression: Feelings of depression often accompany withdrawal from brown sugar addiction. The Brain chemistry can be affected by the absence of the drug, leading to a low mood, sadness, and a sense of hopelessness.
7. Frustration: Frustration is a common emotional response during withdrawal. The individual may experience heightened levels of irritability, impatience, and a general sense of frustration as they cope with the physical and emotional challenges of withdrawal.
8. Lack of concentration and irritability: Brown sugar withdrawal can result in difficulties with concentration and an overall sense of irritability. The individual may find it challenging to focus on tasks or maintain attention, further exacerbating feelings of frustration.
9. Watering of the nose: Another physical symptom that can occur during brown sugar withdrawal is watering of the nose. This may manifest as a runny nose or excessive nasal secretions.
Note: It’s important to note that withdrawal symptoms can vary in intensity and duration depending on the individual, the severity of the addiction, and other individual factors.
Seeking professional help and support is crucial during the withdrawal process to manage these symptoms effectively and increase the chances of successful recovery.
Treatment Of Brown Sugar Addiction
The treatment of brown sugar addiction typically involves a comprehensive approach that addresses the physical, psychological, and social aspects of addiction. Here are some common components of treatment for brown sugar addiction:
1. Detoxification: The first step in treating brown sugar addiction is often detoxification, which involves safely managing withdrawal symptoms as the drug is eliminated from the body. Medical supervision and support may be necessary to ensure the individual’s safety and comfort during this process.
2. Medication-assisted treatment: Medications may be used as part of the treatment plan to help manage cravings, alleviate withdrawal symptoms, and support long-term recovery. Medications like methadone, buprenorphine, or naltrexone can be prescribed under medical supervision.
3. Behavioral therapies: Behavioral therapies are essential for addressing the psychological aspects of addiction. These therapies help individuals identify and modify unhealthy thoughts, behaviors, and patterns associated with drug use. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), motivational interviewing, and contingency management are commonly used approaches.
4. Support groups: Participation in support groups such as Narcotics Anonymous (NA) or similar 12-step programs can provide ongoing support, guidance, and a sense of community during the recovery process. These groups allow individuals to connect with others who have experienced similar challenges and share their journey to recovery.
5. Individual counseling: Individual counseling sessions with a qualified therapist or addiction counselor can provide personalized support and guidance in addressing underlying issues, developing coping strategies, and setting goals for recovery.
6. Family involvement: Involving family members in the treatment process can be beneficial, as it helps create a supportive and understanding environment for the individual in recovery. Family therapy or educational programs can help improve communication, rebuild relationships, and provide the necessary support system.
7. Holistic approaches: Complementary and alternative therapies, such as yoga, meditation, art therapy, or exercise programs, can be integrated into the treatment plan to promote overall well-being, reduce stress, and enhance the recovery process.
8. Aftercare planning: Developing a comprehensive aftercare plan is crucial to support ongoing recovery. This may include ongoing therapy, participation in support groups, regular check-ins with healthcare professionals, and strategies to prevent relapse.
Note: It’s important to remember that treatment should be tailored to meet the individual’s specific needs and may require a combination of approaches.
Seeking professional help from addiction specialists or treatment centers can provide a structured and supportive environment for individuals seeking to overcome brown sugar addiction.
How To Avoid Sugar Addiction?
Prevention plays a crucial role in avoiding brown sugar addiction. By implementing preventive measures, individuals can reduce the risk of developing an addiction to brown sugar or other substances. Here are some key prevention strategies:
1. Education and awareness: Promote public awareness about the dangers and risks associated with brown sugar addiction. Educate individuals, especially young people, about the harmful effects of drug use, including brown sugar. Provide accurate information about the consequences of addiction and the importance of making healthy choices.
2. Life skills development: Encourage the development of essential life skills, such as problem-solving, decision-making, stress management, and coping mechanisms. These skills can empower individuals to handle challenges and make positive choices, reducing the likelihood of turning to drugs as a solution.
3. Parental involvement: Promote open communication and strong relationships between parents or guardians and their children. Parents should educate themselves about the risks of substance abuse, engage in regular conversations with their children about drugs, and provide guidance and support in making healthy decisions.
4. Peer influence: Encourage positive peer relationships and foster a supportive environment among friends and peers. Promote activities and interests that are drug-free and encourage social connections based on healthy lifestyles.
5. Mental health support: Address mental health concerns and provide access to mental health resources. Promote emotional well-being and provide appropriate support and intervention for individuals struggling with stress, anxiety, or other mental health issues, as these can contribute to substance abuse.
6. Community involvement: Engage the community in prevention efforts by organizing awareness campaigns, hosting educational events, and establishing support networks. Collaborate with schools, community organizations, and local authorities to implement preventive measures and create a drug-free environment.
7. Regulation and enforcement: Implement strict regulations and enforcement measures to control the availability and distribution of drugs. Focus on dismantling drug trafficking networks and ensuring that legal consequences are enforced to deter drug abuse.
8. Media and advertising: Monitor and regulate media and advertising content to minimize the promotion and glamorization of drug use. Promote responsible media portrayals and encourage media platforms to discourage the depiction of drug use as attractive or acceptable.
9. Access to treatment and support: Ensure that adequate treatment and support services are available and accessible to individuals struggling with drug addiction. This includes providing information about available resources, treatment options, and support groups for those seeking help.
10. Early intervention: Identify and address risk factors and warning signs of substance abuse at an early stage. Implement intervention programs in schools and communities to provide support and guidance to individuals showing early signs of drug experimentation or risky behaviors.
Note: By implementing a comprehensive prevention approach that addresses multiple factors, including education, support, and community involvement, it is possible to reduce the incidence of brown sugar addiction and promote healthier, drug-free lifestyles.
Frequently Asked Questions on Brown Sugar
1. What is brown sugar?
Brown sugar, in the context of drug addiction, refers to an adulterated form of heroin. It is a street name used to describe a drug that contains a mixture of heroin (usually around 20%) and various impurities or cutting agents.
2. How is brown sugar different from other forms of heroin?
Brown sugar is typically cheaper and less pure compared to other forms of heroin. It gets its name from its brown or dark brown color, which is a result of the impurities mixed with the heroin.
3. How is brown sugar consumed?
Brown sugar can be consumed through various methods, including smoking, snorting, or injecting. The preferred method may depend on the purity and form of the drug available.
4. What are the street names for brown sugar?
Brown sugar is known by several street names, including smack, H, junk, horse, and black tar.
5. What are the risks and dangers of using brown sugar?
Using brown sugar poses significant risks to an individual’s health and well-being. The impurities mixed with the heroin can lead to various health complications.
Brown sugar addiction can result in physical and psychological dependence, deteriorating mental health, financial problems, relationship issues, and an increased risk of overdose and death.
6. Are there any immediate effects of using brown sugar?
When brown sugar is consumed, whether, through smoking, snorting, or injecting, there can be immediate effects such as a rush of euphoria, drowsiness, relaxation, and pain relief. However, these effects are often followed by negative symptoms and side effects.
7. What are the long-term effects of brown sugar addiction?
The long-term effects of brown sugar addiction can be severe and debilitating. They may include respiratory problems, cardiovascular issues, liver and kidney damage, infectious diseases (due to sharing needles), mental health disorders, cognitive impairment, and a decline in overall physical and mental well-being.
8. Can brown sugar addiction be treated?
Yes, brown sugar addiction can be treated. Treatment typically involves a combination of medical detoxification, counseling, behavioral therapies, support groups, and aftercare programs.
It is essential to seek professional help from addiction specialists or treatment centers to develop an individualized treatment plan.
9. Is it possible to recover from brown sugar addiction?
Recovery from brown sugar addiction is possible with the right support, treatment, and commitment. It may be a challenging journey, but with professional help, a strong support system, and personal determination, individuals can overcome addiction and lead fulfilling, drug-free lives.
10. How can I help someone who is addicted to brown sugar?
If you know someone who is struggling with brown sugar addiction, it is important to approach them with compassion and understanding.
Encourage them to seek professional help and offer your support in finding suitable treatment options. Be a source of encouragement and avoid enabling their addiction.
Remember that addiction is a complex issue, and professional assistance is often necessary for successful recovery.


























